Definition
Periodontitis is a chronic inflammation of the gums. The disease begins with gingivitis, an inflammation of the gum line caused by bacterial plaque. The consequences of periodontitis are serious: bone loss occurs at the gum line, leading to the formation of gum pockets. Without treatment, the teeth lose their chewing strength until they have to be extracted.
Periodontology is the branch of dentistry that studies all the tissues around the tooth, in particular the gums and alveolar bone. Periodontal diseases are generally chronic and asymptomatic.

How to treat and prevent gingivitis?
With scaling and brushing measures reviewed according to the patient and their risks, gingivitis can be easily reversed through scaling.
These new oral hygiene habits will serve as a basis for maintaining healthy gums.
In short, the best way to fight this disease is to adopt good daily oral hygiene, in order to eliminate dental plaque before it turns into tartar.
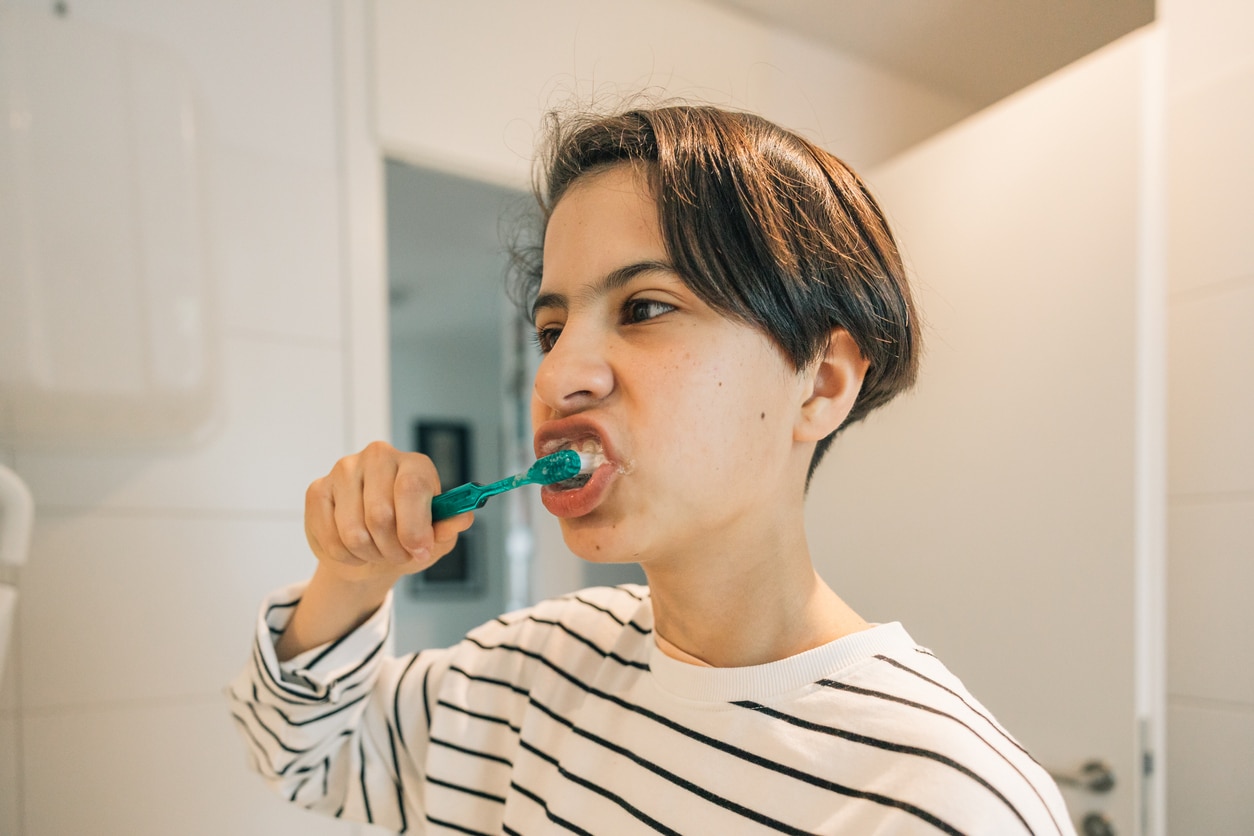

Excellent oral hygiene is essential
Daily brushing with a soft toothbrush and toothpaste that helps to emulsify plaque, morning and evening.
The oral cavity is the first point of entry for bacteria into the body.
Interdental brushes should be used to supplement toothbrushing in most patients, as they enable cleaning between the teeth, where caries and gum inflammation mainly develop.
We also recommend using a tongue scraper once a week, especially for patients who smoke.
Our other treatments
Make an appointment at one of our two clinics