Definition

The tasks of the paediatric dentist
- Routine consultations
- Dental hygiene prevention and instruction
- Preventive care
- Treatment of tooth decay
- Extractions
- Dental emergencies
In addition, the paediatric dentist works closely with the orthodontist and can thus identify your child’s needs in terms of jaw growth and tooth alignment.

Making dental treatment less dramatic
The medical environment can sometimes be intimidating, especially for children. The valuable expertise of the paediatric dentist, trained in pain management and a child-friendly psychological approach, is based on gentleness and a sense of pedagogy. The paediatric dentist ensures that treatment is carried out in a climate of trust and cooperation.
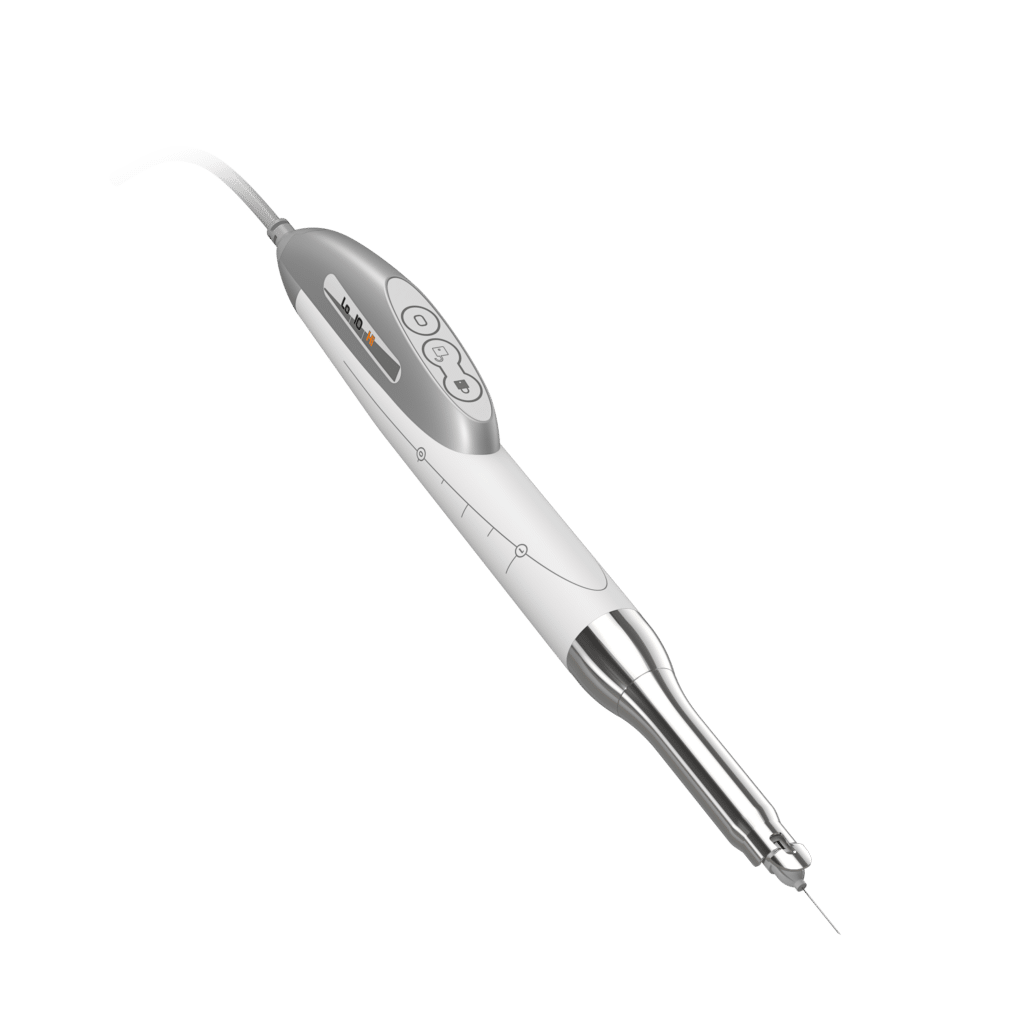
The Quicksleeper: for pain-free anaesthesia
The QuickSleeper is an innovative electronic system designed for the administration of intra-osseous anaesthesia in dentistry.
It offers the following advantages:
- Greater efficiency
- : The anaesthesia is immediate, allowing for procedures without waiting time.
- Comfort for the patient: The injection is virtually painless and the absence of numbness in the soft tissues makes for a more pleasant post-operative experience.
- Precision: Electronic injection control allows precise administration of the anaesthetic, reducing the risk of overdose or anaesthetic failure.
- Versatility: Suitable for various dental procedures, including extractions, endotonic treatments an procedures on children.
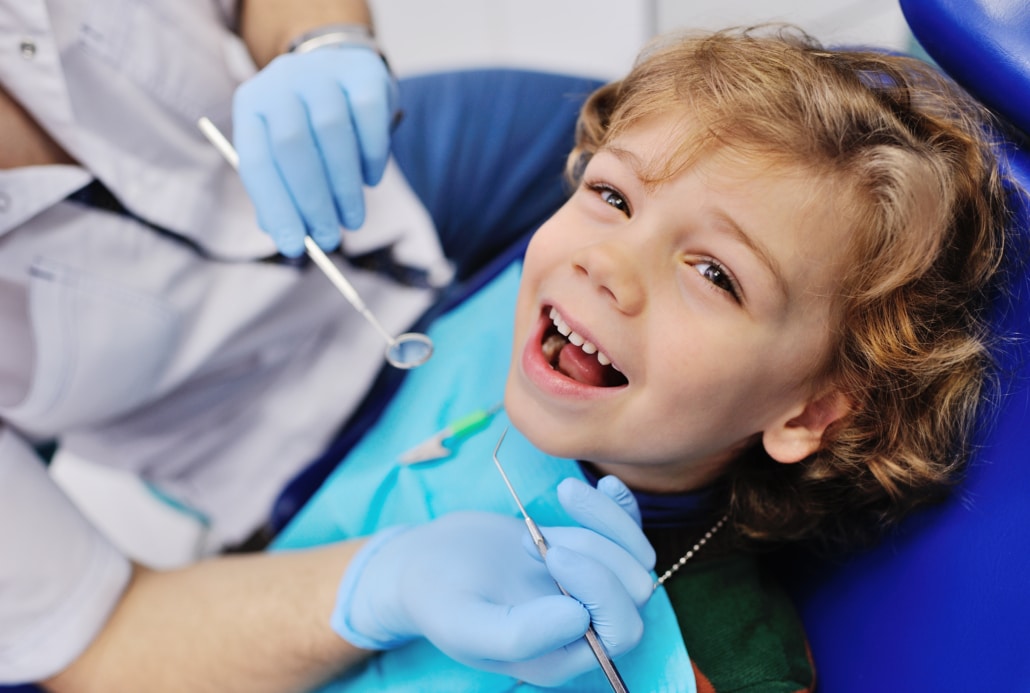
The first consultation
The first consultation is at the heart of a good relationship between the young patient and their dentist. It allows the child to gain confidence and the dentist to give the parents the main information. This diagnostic visit consists of a complete oral examination and X-rays if necessary. This first visit takes place at around three years of age, which allows for an initial contact without the issue of treatment. A check-up every six months to a year is essential to ensure good oral health for your children and to monitor the change from milk teeth to permanent teeth.
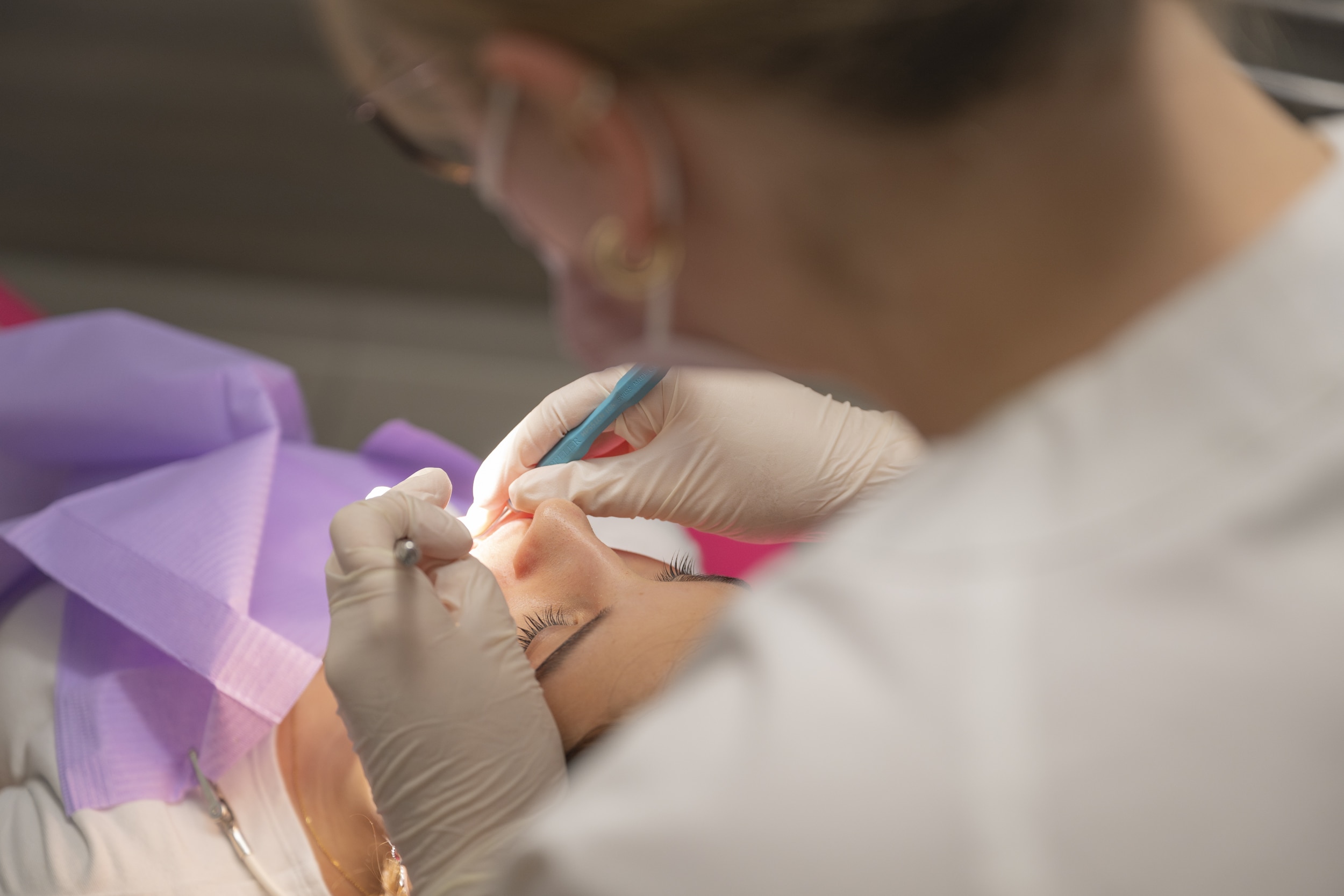
Preventive care
Preventive care includes fissure sealing of the permanent molars, which is effective in preventing possible cavities when these teeth erupt from the age of six.

Treatment of milk teeth
Milk teeth (or temporary teeth) play an essential role in children’s oral health. They enable chewing, phonation and provide space for the permanent teeth. Although they are temporary, their treatment is crucial to prevent future complications.
Make an appointment at one of our two clinics


